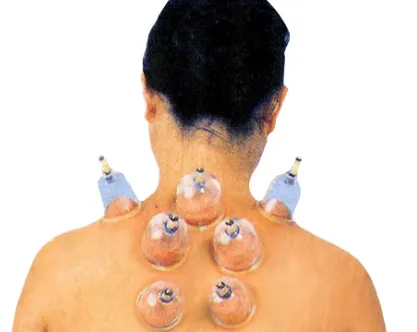
General Detox with 7 Organ Hijama Points

The seven-organ Hijama points are essential in maintaining the body’s natural healing process. The seven-organ Hijama points hold significant importance in cupping therapy due to their direct and indirect connection to vital internal organs. These specific points are strategically chosen to stimulate detoxification, regulate organ function, and restore balance in the body. Each of these points corresponds to a major organ such as the liver, lungs, kidneys, heart, stomach, bladder, and intestines. Locations of these Hijama Points Hijama Point no 1: Top of the spine and back of the neck on the shoulder blade Hijama Point no 4: located on the upper back, on the right side of the shoulder blade. Hijama point no 5: mirror of point 4, on the left side of the shoulder blade. Hijama point no 22: located in the middle of the back, on the right side of the spine. Hijama point no 23: mirror of point 22, on the left side of the spine. Hijama point no 24: located in the lower back/pelvis, fur...